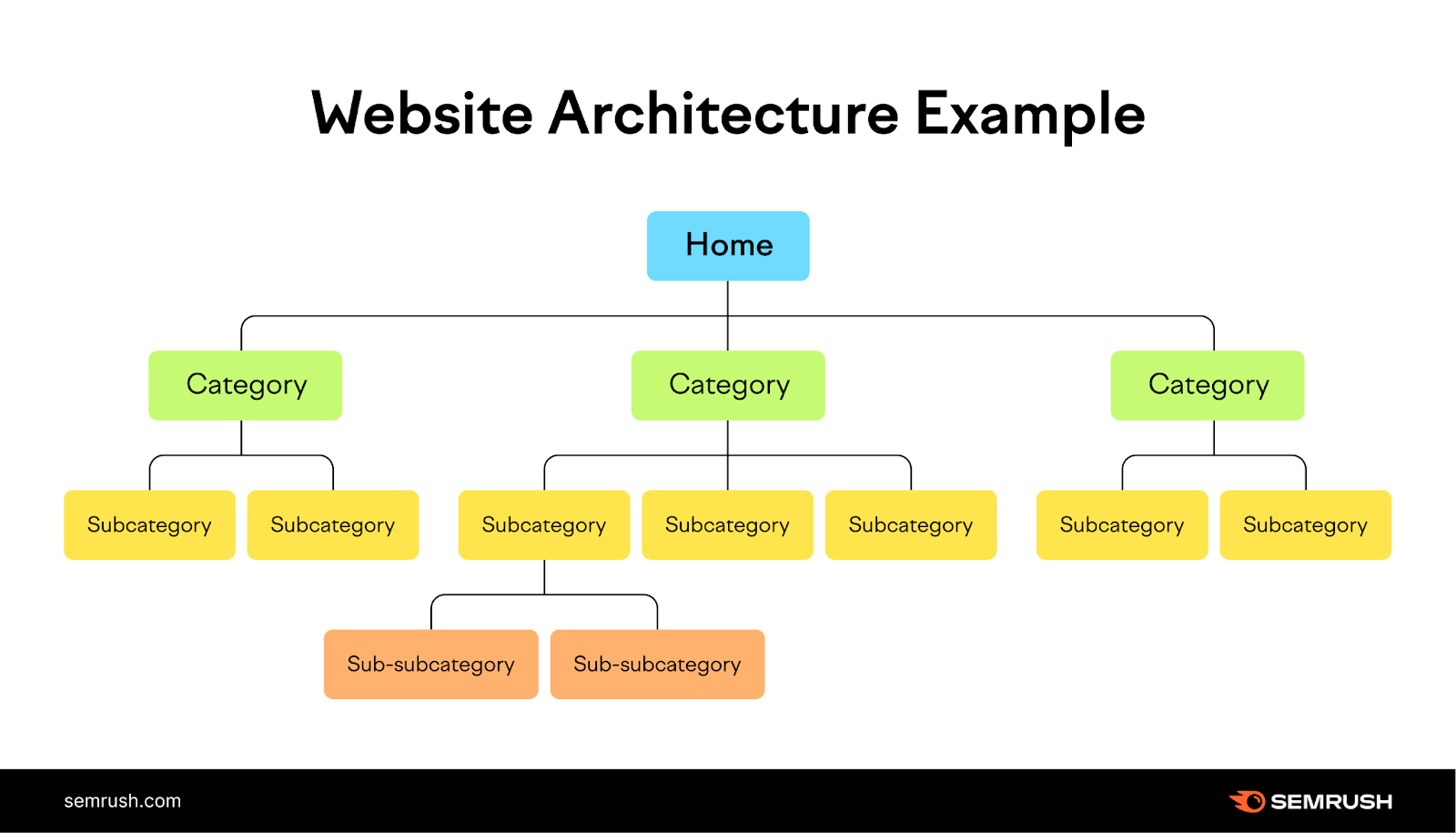
Site architecture is a critical factor that influences how search engines index web pages. It determines the ease with which both search engines and users navigate a website. A well-structured site architecture enhances indexing depth, ensuring that all pages are discoverable and accessible. By optimizing elements like internal linking and URL structure, site owners can effectively guide search engine crawlers throughout their site, improving visibility and ranking potential. Addressing indexing depth involves understanding how architecture impacts crawling efficiency and how strategic design can lead to better search engine performance, ultimately driving more traffic and engagement to a website.
Understanding the Role of Site Architecture in Indexing Depth
Site architecture plays a significant role in how search engines index web pages. A well-structured site facilitates efficient crawling and deep indexing, enhancing site visibility and search engine ranking. Conversely, poor architecture can limit indexing depth, meaning not all pages are easily accessible or indexed by search engine bots. Below, we explore the various aspects of site architecture that affect indexing depth.
Importance of a Flat Site Structure
A flat site structure is a strategic design where every page is only a few clicks away from the homepage. This minimizes the depth of websites, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index content effectively. A flatter structure ensures that more pages are indexed quickly, which is crucial for large sites with expansive content. By keeping essential content close to the root, you increase the chances of those pages being indexed and retrieved by users promptly.
URL Structure and Its Impact on Indexing
The URL structure significantly influences how search engines interpret and index web pages. Clean, descriptive URLs that use keywords effectively can enhance indexing depth by providing clear context about the page content. Hierarchical URLs reflecting the site’s architecture help bots understand the relationship between different pages, improving crawl efficiency. Furthermore, consistent URL structures can prevent indexing conflicts, such as duplicate content issues, which can arise from complex or poorly managed URLs.
Internal Linking Strategy for Better Crawlability
An effective internal linking strategy is essential for guiding search engines through your site’s content. Internal links distribute page authority and help search engines discover and index new or less visible parts of a site. By strategically linking to priority pages from high-authority pages, you ensure deeper and more comprehensive indexing. A sitemap, which is a model of a site’s content, also aids in this process by providing a roadmap for crawlers to follow.
Site Speed and Its Role in Indexing Depth
Site speed affects not only user experience but also search engine crawling efficiency. Fast-loading sites enable crawlers to navigate and index pages more thoroughly within their allocated crawl budget. Slow-loading or resource-heavy sites may see lesser pages crawled within a given timeframe, resulting in poor indexing depth. Optimizing site performance by compressing images, leveraging browser caching, and minimizing JavaScript can significantly enhance crawling and indexing rates.
Mobile Responsiveness as an Indexing Factor
With the rising trend of mobile-first indexing, mobile responsiveness has become a critical component of site architecture. Responsive designs ensure that web pages are adaptable across different devices, improving user experience and crawl accessibility. Sites that are not mobile-friendly may experience limited indexing depth as search engines prioritize mobile-friendly sites for their mobile-search index. This makes ensuring a responsive design integral for maintaining comprehensive indexing and search visibility.
| Site Architecture Element | Impact on Indexing Depth |
|---|---|
| Flat Site Structure | Enables quick access to all pages, ensuring more pages are indexed. |
| URL Structure | Clear and hierarchical URLs aid in proper page indexing and context understanding. |
| Internal Linking | Facilitates page discovery and passing of page authority to improve indexing. |
| Site Speed | Improves crawling efficiency, allowing more pages to be indexed. |
| Mobile Responsiveness | Essential for mobile-first indexing, ensuring content is easily accessible on all devices. |
What is website structure in SEO?

Website structure in SEO refers to how the different pages on a website are organized and linked together. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that search engines can easily crawl and index the website, as well as providing a seamless user experience. A well-structured site not only helps search engines understand your content better but also aids in guiding visitors to the information they are looking for.
Importance of a Solid Website Structure for SEO
A robust website structure is vital for several reasons:
- Improved Crawl Efficiency: Search engines like Google use bots to crawl websites and understand their content. A clear structure ensures that bots can efficiently navigate through the site, enhancing the discoverability of all your pages.
- User Experience: A well-organized site simplifies navigation for users, ensuring they can quickly find what they need. This improves user satisfaction and often leads to lower bounce rates and higher engagement.
- Enhanced Link Equity: Structure dictates how link authority flows across your site. A logical hierarchy helps in distributing link equity effectively, boosting the ranking potential of important pages.
Components of an Effective Website Structure
Outlined below are the key components of a well-structured website:
- Hierarchical Organization: Begin with a simple hierarchy where the homepage is at the top, followed by category and subcategory pages. This structure helps both users and search engines understand the relationship between different pages.
- Logical URL Structure: Implement clean and descriptive URLs. These should reflect the site’s hierarchy and include relevant keywords which assist search engines in understanding page content.
- Internal Linking: Use internal links to connect relevant pages. This practice aids in guiding users through your site and allows search engines to easily discover all content. Ensure that your most critical pages have ample internal links.
Best Practices for Optimizing Website Structure for SEO
Follow these best practices to optimize your website’s structure:
- Mobile-Friendly Design: Ensure the site is fully responsive. With the rise of mobile use, a mobile-optimized structure is essential for both user experience and search rankings.
- Sitemap Creation: Create and submit an XML sitemap to search engines. This promotes better indexing by allowing bots to easily find your site’s pages.
- Breadcrumbs Navigation: Implement breadcrumbs to help users track their location within the website. This element not only enhances navigation but also provides additional context to search engines about the site’s structure.
How does site indexing work?
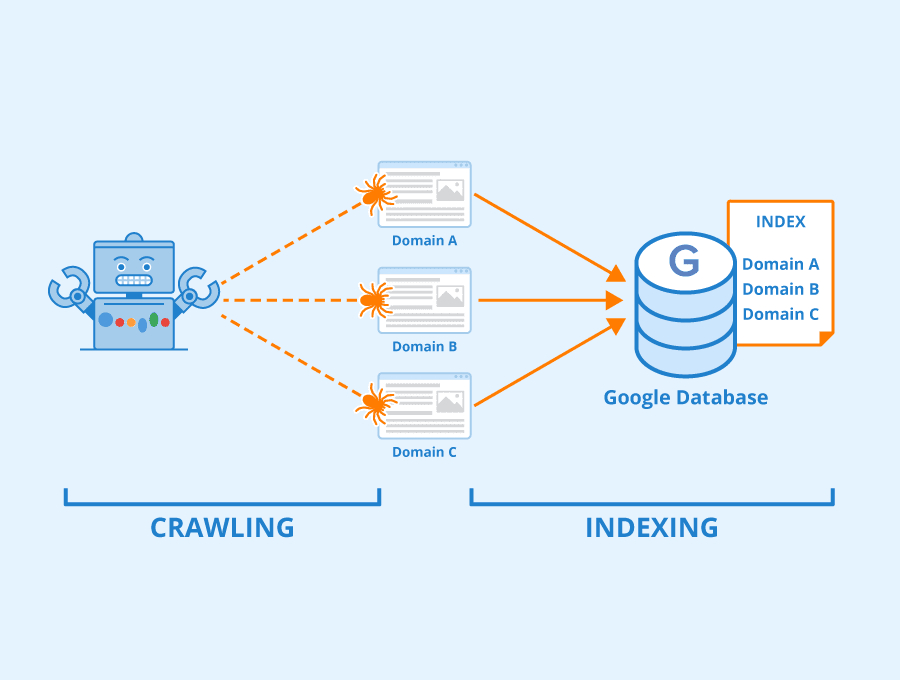
What is Site Indexing?
Site indexing is the process by which search engines organize and make sense of the vast amounts of information available on websites, so it can be retrieved and displayed to users in search results. When a website is indexed, its content becomes part of the search engine’s database.
- Crawling: Search engines use robots or spiders to traverse the web and discover new and updated web pages. These bots follow links to gather data.
- Parsing: Once a page is crawled, the data is extracted and analyzed. This involves looking at metadata, keywords, and the structure of the content.
- Storing: The information collected is stored in the search engine’s index, which is essentially a giant database that can be quickly queried to produce relevant search results.
How Do Search Engines Determine What to Index?
Search engines use various algorithms to decide which pages should be included in the index. These algorithms assess and prioritize web pages based on several factors to ensure the most relevant and valuable content is accessible to users.
- Relevance: The content must be relevant to the user’s search queries. This is determined through keyword analysis and the content’s overall relation to potential search phrases.
- Authority: Pages that are considered authoritative, such as those with a high number of quality backlinks, are more likely to be indexed prominently.
- Structure and Accessibility: Proper HTML formatting, use of semantic tags, and a mobile-friendly design contribute to a page’s likelihood of being indexed.
What Can Affect Site Indexing?
Various factors may impact whether and how well a site is indexed by search engines. Understanding these can help in optimizing a website for better indexing performance.
- Blocked Resources: If a site’s robots.txt file restricts access to certain areas or resources, these portions won’t be crawled or indexed.
- Dynamic Content: Pages that rely heavily on JavaScript or asynchronous content loading might be more challenging to index.
- Duplicate Content: Content that is duplicated across multiple URLs can confuse search engines, possibly affecting indexing and ranking negatively.
How does site structure affect SEO?
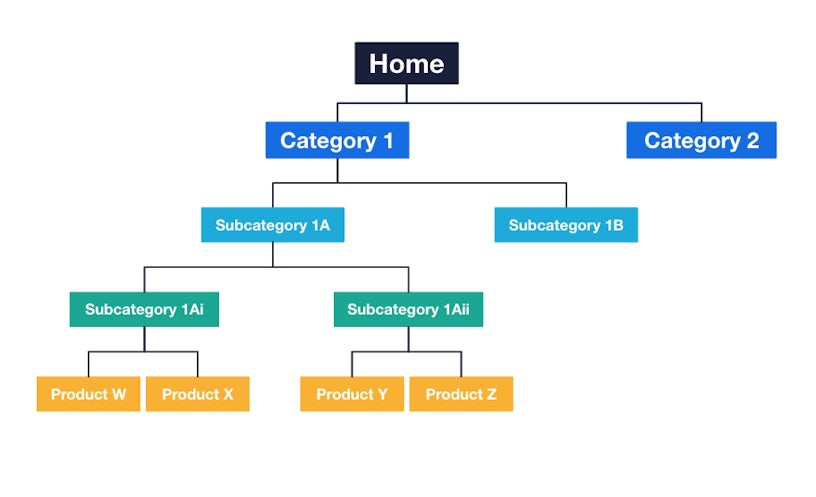
Site structure plays a crucial role in Search Engine Optimization (SEO) by influencing both user experience and how search engines interpret your website. A well-structured site ensures that your content is easily navigable and accessible, enhancing your chances of ranking higher in search engine results. Below are three important aspects of how site structure impacts SEO.
Improves Crawlability
A well-organized site structure makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index your website. Here’s how it works:
- Logical Hierarchy: A clear hierarchy—from homepage to categories to individual pages—helps search engines understand the importance of each section of your site.
- Internal Linking: Proper internal linking helps distribute link equity throughout the site, allowing search engines to find new and existing pages efficiently.
- XML Sitemaps: Including a sitemap guides search engines to all the important pages of the site, ensuring nothing significant is overlooked.
Enhances User Experience
A structured website offers a better user experience, which indirectly influences SEO rankings. Consider the following points:
- Easy Navigation: Clearly defined navigation menus reduce bounce rates by helping users find the information they need quickly.
- Consistent Layout: A uniform layout across pages ensures a seamless user experience, encouraging visitors to explore further.
- Faster Load Times: A streamlined structure often leads to quicker site load times, a factor that search engines consider for ranking.
Helps in Keyword Targeting
Your site structure impacts the efficiency of keyword targeting strategies. Here’s how it helps:
- Categorization: By categorizing content areas, you can target specific keywords more efficiently within each category.
- URL Structure: Clean URLs with relevant keywords contribute to better rankings and involve users in a more intuitive navigation.
- Breadcrumbs: Use breadcrumbs to improve navigation and ensure that search engines understand the page hierarchy and relationships better.
How to build site architecture?

To build effective site architecture, it’s essential to establish a framework that not only enhances user experience but also improves search engine optimization (SEO) and facilitates easy navigation. Here’s a comprehensive approach to building site architecture.
Understand User Needs and Behaviors
Before starting to build your site architecture, understanding your user’s needs and behaviors is crucial. This will guide you in organizing content that aligns with their expectations.
– User Research: Conduct interviews, surveys, or use analytics tools to gather data on what your users are seeking.
– User Personas: Develop user personas to pinpoint the types of users visiting your site and their specific goals.
– User Journey Mapping: Map out the typical journey of your users to visualize the paths they take through your site.
Organize Content Hierarchically
A well-organized hierarchical structure allows users and search engines to navigate your site more effectively.
- Primary Categories: Define broad categories that encompass the main topics covered on your site.
- Subcategories: Break down primary categories into more specific subcategories to refine the content organization.
- Pages: Under each subcategory, create pages that delve into specific topics, ensuring each page is only a few clicks away from the homepage.
Create a Consistent and Intuitive Navigation Menu
A consistent and intuitive navigation menu is essential for guiding users effortlessly through your site.
- Simplicity: Keep the navigation menu simple with clear and descriptive labels that are easy to understand.
- Consistency: Use the same navigation elements across all pages to ensure consistency and familiarity.
- Prioritize Key Pages: Highlight and prioritize the most important pages in your navigation menu, making them more accessible.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is site architecture and how does it influence indexing depth?
Site architecture refers to the way a website’s pages are organized and linked together. A well-structured site architecture helps search engines crawl and index the website more efficiently. Effective site architecture ensures that all pages are easily accessible, thereby enhancing indexing depth. Proper internal linking and a logical hierarchy ensure that even the deepest pages on a website are more likely to be indexed. If a site’s architecture is poorly planned, search engines might find these pages less accessible, potentially impacting their inclusion in search results.
How can clear navigation improve a website’s indexing depth?
Clear navigation is crucial in improving a website’s indexing depth as it guides both users and search engines through the site’s content. With a well-defined navigation structure, pages are easier to find, making it less likely that any page will be orphaned or difficult for search engines to index. Features like breadcrumb trails, intuitive category pages, and consistent menu structures emphasize important areas of the site and ensure all content is reachable within a few clicks, thereby enhancing the probability of each page being indexed by search engines.
Why is internal linking important for effective site architecture?
Internal linking plays a pivotal role in effective site architecture because it provides direct pathways between various pages of a website, distributing link equity and authority across the site. This not only aids users in navigating through the content but also enables search engines to discover and index more pages. Strategically placed internal links ensure that important pages are easily found and given priority in indexing. By linking less prominent pages directly from more authoritative ones, their visibility to search engines is greatly improved, aiding in a deeper and more thorough indexing process.
How does URL structure contribute to better indexing of a site?
A well-designed URL structure is critical for better indexing as it helps define the hierarchy and context of a website’s content. Readability and maintaining a logical URL format contribute significantly to how search engines interpret page relationships. URLs that are concise and descriptive provide clear indicators to search engines about the content of a page. Ensuring that every URL is unique and follows a coherent pattern aids search engines in navigating through and understanding a website’s architecture, ultimately facilitating more comprehensive and efficient indexing.