Understanding the nuances between crawl frequency and indexing frequency is crucial for optimizing website performance and visibility. While both aspects are integral to search engine dynamics, they serve distinct functions. Crawl frequency refers to how often search engine bots visit a website to discover new or updated content. In contrast, indexing frequency involves the addition of web pages to a search engine’s database after they are crawled. These processes, though interconnected, impact a site’s visibility in search results differently. This article delves into the key differences between these two elements, exploring how they can influence SEO strategies and website management.
Crawl Frequency vs. Indexing Frequency: Understanding the Differences
When dealing with Search Engine Optimization (SEO), it’s crucial to understand the distinctions between crawl frequency and indexing frequency, as these processes significantly impact how often and how well your website content is recognized and displayed in search engine results.
Understanding Crawl Frequency
Crawl frequency refers to how often search engine crawlers, like Google’s Googlebot, visit a website to discover content. These bots analyze the website’s structure, update existing pages, find new pages, and ensure current content’s credibility. The frequency can vary based on several factors: 1. Website Popularity: More popular sites tend to be crawled more frequently. 2. Content Freshness: Frequently updated content attracts more frequent crawling. 3. Server Performance: Efficient server response speeds can increase crawl frequency. 4. Site Structure: A complicated structure can hinder effective crawling.
Understanding Indexing Frequency
The term indexing frequency refers to how often crawled content is evaluated and added to a search engine index, making it available for users to find in search results. This process determines the time it takes for new or updated content to be visible online. Indexing frequency is influenced by: 1. Content Quality: High-quality content is indexed more reliably. 2. Relevance: Content that’s seen as highly relevant to topics of interest will be prioritized. 3. Meta Tags: Properly defined meta tags can streamline the indexing process. 4. Existing SEO Strategy: Websites with optimized SEO strategies experience better indexing rates.
Key Differences Between Crawl and Indexing Frequency
The key differences between crawl and indexing frequency lie in their objectives and processes. While crawl frequency is concerned with how often the website is visited by bots, indexing frequency is focused on how quickly and accurately the content is processed and made available in search results. Both play critical roles in: – Visibility: Ensuring that updated content appears in search engines promptly. – SEO Performance: Both processes impact overall SEO performance differently. – Content Discovery: Crawling discovers content while indexing ensures discoverability in search results.
Factors Influencing Crawl Frequency
Several factors influence the crawl frequency of a website, including: – Technical SEO: Implementing a sitemap and robots.txt can guide and improve crawling. – Link Structure: Internal and external linking can enhance crawl efficiency and coverage. – Error Rates: High error rates can deter frequent crawling as they reduce overall crawl budget.
Factors Influencing Indexing Frequency
The frequency at which content is indexed is influenced by elements such as: – Page Speed: Faster page speeds can increase the attractiveness of content for quick indexing. – Duplicate Content: Avoiding duplicate content enhances indexing frequency and effectiveness. – Canonical Tags: Proper use of canonical tags can prevent indexing issues with duplicate content.
| Aspect | Crawl Frequency | Indexing Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Discover and analyze website content | Evaluate and make content searchable |
| Influence on SEO | Ensures content is known by search engines | Ensures content is displayed in search results |
| Key Factors | Popularity, Freshness, Server Performance | Quality, Relevance, Meta Tags |
| Challenges | Complicated site structures | Duplicate content |
| Optimization Techniques | Sitemaps, Internal Linking | Page Speed, Canonical Tags |
What is the difference between crawling and indexing?
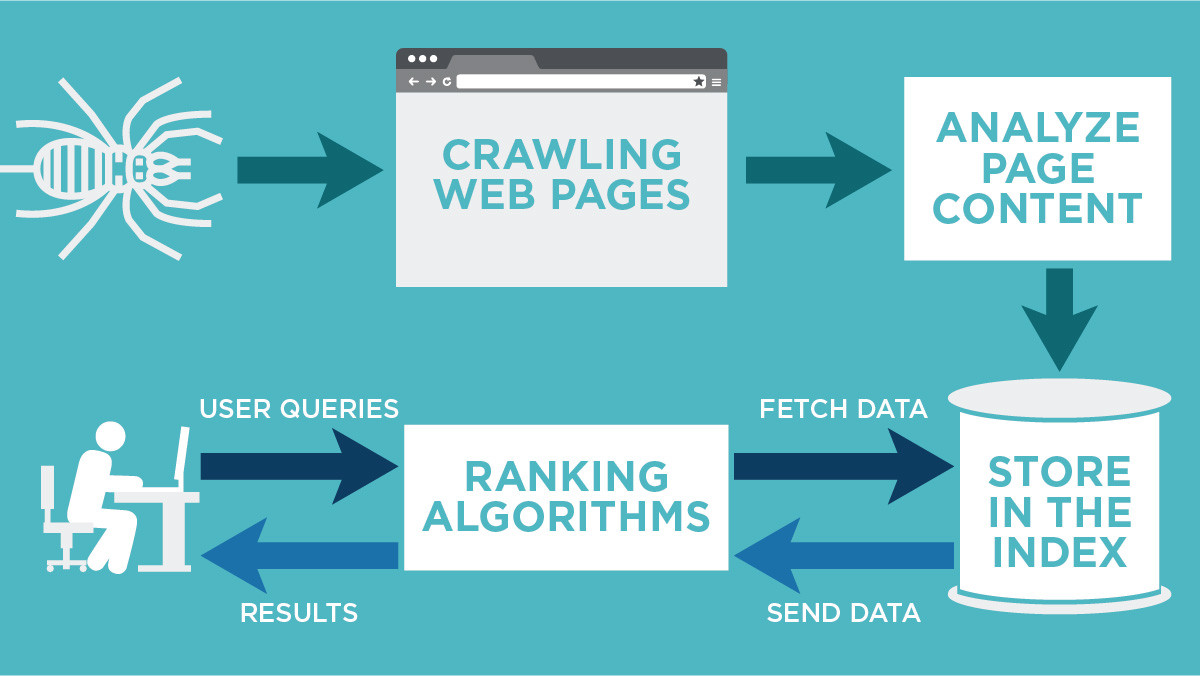
Crawling: The Initial Step in Search Engine Process
Crawling refers to the process by which search engines discover new and updated content on the web to build a comprehensive index. This is done through automated programs known as crawlers or spiders. These programs systematically browse the internet, following links and identifies worthy content to include in the search engine’s databases.
- Crawlers: These are automated bots that visit sites and report back with data about them.
- Link Following: They follow links from one webpage to another, discovering new URLs.
- Content Discovery: Crawlers find new pages and refresh the data of already known pages.
Indexing: Organizing the Discovered Data
Indexing involves analyzing the data discovered during the crawling process and organizing it in a way that makes it easily retrievable by the search engine when queries are entered. This process allows search engines to provide relevant results quickly by storing key information about the website content.
- Data Analysis: This involves processing and categorizing the content of the webpage.
- Keyword Assignment: Keywords and metadata are cataloged for efficient query matching.
- Database Storage: The indexed content is stored in databases for fast retrieval.
Key Differences Between Crawling and Indexing
Understanding the differences between crawling and indexing can clarify how search engines operate and rank websites. While both are crucial to search engine functionality, they serve distinct purposes and involve different types of processing.
- Purpose: Crawling is aimed at discovering pages, whereas indexing involves organizing data.
- Process: Crawling uses bots to gather data; indexing involves algorithmic sorting and storage.
- Outcome: Crawling results in new or updated web pages being found; indexing makes these pages searchable.
What is the difference between indexer and crawler?

Understanding the Role of a Crawler
A crawler, often referred to as a spider or bot, is a crucial part of search engine technology. It is designed to systematically browse the internet and collect data on web pages. Here’s what a crawler does:
- Discovery: Crawlers start by visiting known web pages and follow links on these pages to discover new URLs, thus expanding their scope of visitation.
- Data Collection: They collect data from each page such as the text, images, metadata, and the relationships between pages through links.
- Scheduling Visits: Crawlers return periodically to previously visited pages to check for updates or changes, ensuring the most current content is captured.
The Purpose of an Indexer
An indexer takes the data collected by the crawler and processes it so that it can be efficiently searched and retrieved. Here’s how an indexer operates:
- Data Organization: The indexer processes the data into a structured format, categorizing content by keywords and themes to aid in quick retrieval.
- Relevance Ranking: It evaluates the importance of content by analyzing factors like keyword density, location, and page links to determine its relevance in search results.
- Storage in Databases: Indexers store the organized data in massive databases that search engines query when a user performs a search.
Key Differences Between Indexers and Crawlers
While both crawlers and indexers work together within search engines, they serve distinct functions. Here’s a breakdown of their differences:
- Function: Crawlers are tasked with discovering and collecting raw data from web pages, whereas indexers process and organize this data into searchable formats.
- Operation Timeframe: Crawlers operate continuously, exploring and revisiting the internet, while indexers work in parallel to handle the incoming data.
- Outcome: The end product of a crawler is a collection of web data, while the indexer produces a structured database that aids in delivering relevant search results.
What is the difference between crawlability and Indexability?

Understanding Crawlability
Crawlability refers to a search engine’s ability to access and scan the web pages of a website. This process is the first step in having your pages recognized by search engines. Here are some essential points about crawlability:
- Access: Crawlability ensures that search engine bots can access and navigate through the website’s content without any obstacles, such as robot.txt files or poorly structured internal links.
- Efficiency: With better crawlability, bots can crawl more pages within their allocated crawl budget, enhancing the chances of pages being recognized.
- Barriers: Factors like blocked pages, dead links, or site errors can hinder a bot’s ability to crawl effectively.
Exploring Indexability
Indexability is a step beyond crawlability, focusing on a search engine’s capacity to interpret and store a webpage within its database. It determines whether a crawled page can be understood and added to a search engine’s index. Key points about indexability include:
- Page Content: For a page to be indexable, its content must be comprehensible and relevant to the search engine, with proper use of meta tags and semantic HTML.
- Meta Tags: Tags like ‘noindex’ within the page’s meta can instruct search engines to avoid indexing a page even if it’s crawled.
- Stored Information: Indexation involves storing the page’s data in the search engine’s database for retrieval during a user’s search query.
Key Differences Between Crawlability and Indexability
While crawlability and indexability are crucial for SEO, they have distinct roles in how a page is finally listed in search results. Here’s how they differ:
- Process Sequence: Crawlability is the preliminary step, involving the search engine’s ability to discover a page, whereas indexability concerns adding the page’s content to the search engine’s index.
- Technical Aspects: Crawlability focuses on the structural and accessibility aspects of a website, like site architecture and link health, whereas indexability is about content factors and meta directives.
- Outcome: A well-crawled site might not be indexed if it lacks relevant content or directives are present to prevent it. Indexability requires content that meets search engine criteria.
What happens first, crawling or indexing?

In the process of making web content discoverable and searchable, crawling generally occurs before indexing. Crawling is performed by search engine bots that scan internet content, while indexing is about storing and organizing that content to appear in search results.
Understanding Crawling
Crawling is the first step where search engines send out bots known as spiders or crawlers to discover new and updated content on the web. This process involves:
- Discovering URLs: Crawlers follow links from known pages to discover new URLs.
- Fetching Page Content: After finding the URLs, the bots fetch data to understand what is on the page.
- Checking Updates: Crawlers regularly revisit pages to check for updates or changes to the content.
Understanding Indexing
Indexing occurs after crawling and involves analyzing, processing, and storing the data fetched during the crawling phase to facilitate search results. This includes:
- Analyzing Content: Search engines analyze text, tags, and attributes to understand what the page is about.
- Storing Information: Relevant content is stored in an index database which acts as a massive library of web content.
- Ranking Potential: During indexing, pages are assessed for their relevance and authority, influencing their search ranking.
Why Crawling Comes Before Indexing
The reason crawling comes before indexing is logical and sequential as one cannot store and analyze a page’s data if it hasn’t been found yet. The process is:
- Sequential Discovery: Crawling is necessary to discover pages that can then be indexed.
- Data Collection: Without crawling, there is no data to analyze or store, making indexing impossible.
- Dependency System: Indexing depends on crawled data to ensure search engines have a database of known, discovered URLs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between crawl frequency and indexing frequency?
Crawl frequency refers to how often search engine bots visit a website to check for updates or new content. It’s the process by which these bots scan your site’s pages to gather information. In contrast, indexing frequency pertains to how often these pages are added to the search engine’s index. This step is crucial for pages to actually appear in search results. While crawling generally precedes indexing, it doesn’t necessarily mean that every crawled page gets indexed. A key distinction lies in their purposes: crawling is about discovery, while indexing is about storage and retrieval of useful content.
How does crawl frequency impact website SEO?
Crawl frequency can significantly impact your website’s SEO because it determines how often your website’s new or updated pages are discovered by search engines. High crawl frequency can result in quicker updates to your site being reflected in search engine results, whereas low crawl frequency might delay this process. However, merely having a high crawl frequency doesn’t guarantee better ranking. It’s essential to focus on site health, speed, and architecture to ensure that when your site is crawled, it’s presented in its best form. Well-structured websites with fast load times and optimized content tend to be crawled more frequently.
What factors influence indexing frequency?
Indexing frequency is influenced by several factors, including the overall quality and relevance of content, user engagement metrics, and adherence to SEO best practices. Search engines prioritize indexing websites that provide consistent, high-quality content that meets user intent. Factors such as duplicate content, site errors, or poor navigation structure can negatively impact how frequently and effectively your pages are indexed. Moreover, implementing structured data and fostering user engagement through comments or social sharing can positively influence indexing frequency as these elements signal content value to search engines.
Can crawl frequency be increased, and how?
Yes, the crawl frequency can be increased through several strategies aimed at enhancing your website’s visibility and authority. First, ensure your website’s technical foundation is robust: fast loading times, a responsive design, and a proper sitemap can encourage more frequent crawls. Regularly publishing fresh, relevant content will also attract search engine bots. Moreover, earning more backlinks from reputable sites can signal to search engines that your site is important, prompting them to crawl it more often. Utilizing Google Search Console to submit updated sitemaps and monitoring crawl stats can help you optimize your strategy for increasing crawl frequency.