In the realm of search engine optimization, ensuring that Googlebot has crawled your link is crucial for gaining visibility and driving traffic to your website. Understanding whether or not Google’s own web crawler has indexed your page can significantly impact your strategy for increasing search rankings. This article explores methods to verify if Googlebot has visited your link, offering insights to help webmasters and digital marketers optimize their sites effectively. From leveraging Google Search Console to exploring server logs, these techniques will provide a clear picture of Googlebot’s interaction with your content, enabling you to make data-driven decisions for enhanced online presence.
How to Test If Googlebot Crawled Your Link
To determine whether Googlebot has crawled your link, you need to utilize several techniques and tools designed to provide insights into Google’s crawling activities. Understanding this process gives you a better view of your website’s performance in search engines and the effectiveness of your SEO strategies.
1. Checking Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free tool that offers comprehensive insights regarding how your site performs on Google. – Log into your account and select the property that is associated with your website. – Navigate to the Coverage report. Here you will find various statistics about your site’s URLs, including any Errors, Valid with warnings, Valid, and Excluded URLs. – Click on the Submitted URLs tab to determine if particular pages, such as the one in question, have been indexed or encountered any issues during crawling.
2. Analyzing Server Log Files
Server log files are another effective way to track Googlebot’s activity: – Access your server log files, which record various activities on your web server. – Use a tool like Screaming Frog Log File Analyser or your preferred text editor to search through the logs. – Look for entries that include the user agent Googlebot to confirm its activity. The presence of Googlebot in these logs confirms that it has accessed your pages.
3. Using Google Search Operators
Google search operators can quickly verify if a page is indexed: – Enter the query `site:yourdomain.com/page-url` into Google search. – If the page appears in the search results, it means Googlebot has crawled and indexed your page. – If not, the page may either not be crawled yet or has encountered an indexing issue.
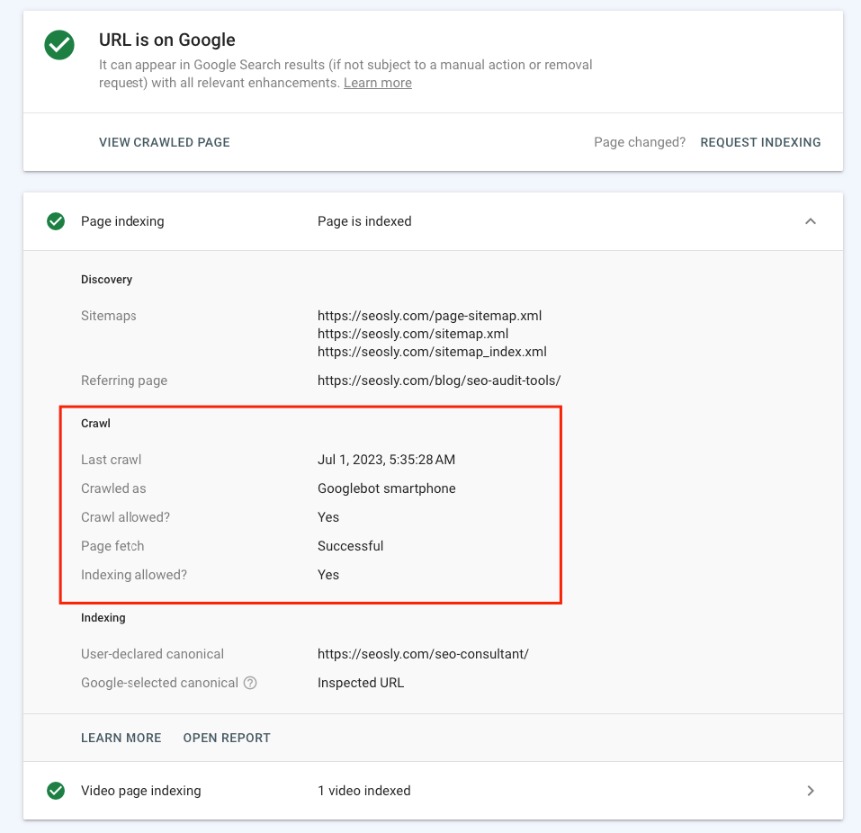
4. Inspecting URL with the URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection Tool within Google Search Console provides specific details about a URL’s indexed version: – Enter the URL in question in the search bar at the top of the Console. – This will show when Google last crawled the page, and any indexing or crawling errors that might be present. – It allows you to request reindexing if necessary.
5. Utilizing Third-Party SEO Tools
Third-party SEO tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz provide additional insights: – These tools often provide reports on how web pages perform, including information about when Googlebot last crawled your page. – Leverage their functions to track rankings, organic traffic, and more, giving a broader overview of how your site is perceived by Googlebot.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Check Coverage report for URL indexing status |
| Server Log Files | Analyze logs for Googlebot activity |
| Google Search Operators | Use site: operator to verify indexing |
| URL Inspection Tool | Detailed URL crawl and issues analysis |
| Third-Party SEO Tools | Track SEO metrics and Googlebot interactions |
How do I check if Google crawled my site?
To check if Google has crawled your site, you need to verify it through various tools and methods that provide data regarding Google’s indexing activities. Here are some steps and related topics:
Use Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free service that allows you to monitor and troubleshoot your site’s presence in Google Search results. Here’s how to check if Google has crawled your site using this tool:
- Verify Site Ownership: First, you’ll need to verify that you own the site by adding it to your Search Console account and verifying it through one of the available methods, such as adding a DNS record or uploading an HTML file.
- Check Crawl Status: Navigate to the “Coverage” report within Search Console. Here, you can see if your site is being crawled and which pages have been indexed or encountered errors.
- Submit a Sitemap: Submitting a sitemap can help Google to better crawl your site. You can do this in the Sitemaps section, and it will improve the efficiency of the crawl.
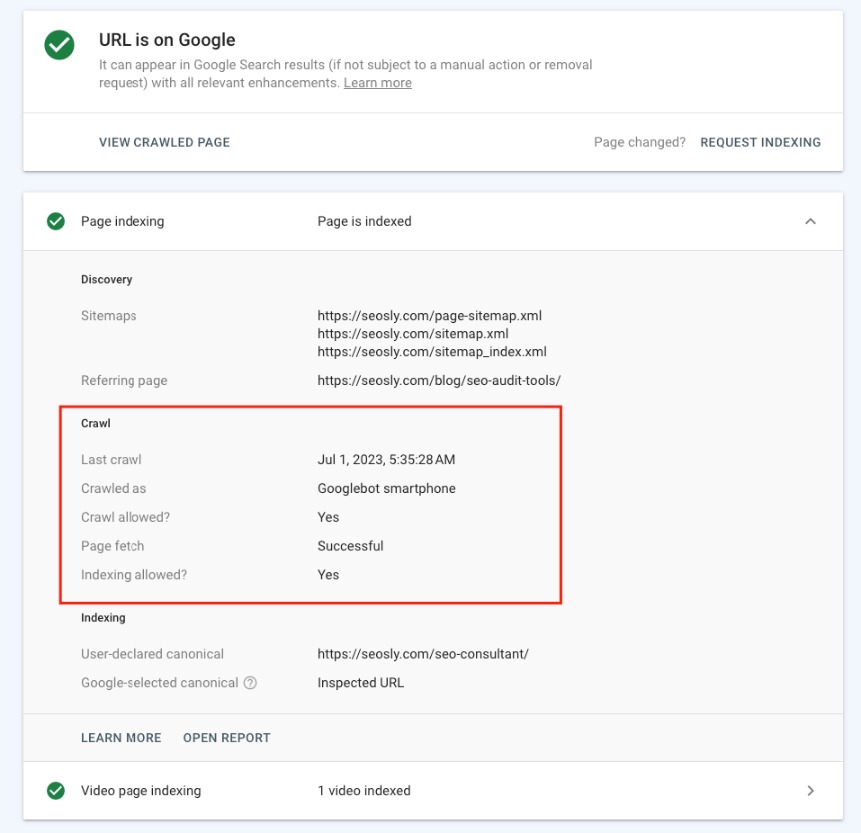
Use URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console provides detailed crawl, index, and serving information about your web pages. Here’s how you can leverage this tool:
- Access the Tool: Within Google Search Console, navigate to “URL Inspection.”
- Analyze Specific URLs: Enter any URL from your website to see if it has been crawled and indexed. You’ll get detailed information about each URL’s status.
- Request Indexing: If the URL isn’t indexed, you can request indexing directly from the inspection interface, prompting Google to crawl the URL at its earliest convenience.
Monitor Server Log Files
Server log files can provide insights into how search engines interact with your site. Here’s how to use them:
- Access Log Files: Host your site on a server where you can access its logs. These files can be large, so ensure you can parse them efficiently.
- Identify Googlebot: Look for entries from the Googlebot user agent in the logs. This indicates that Google’s crawler has accessed your site.
- Analyze Crawl Patterns: Regularly analyze these logs to understand crawl behavior and how often Googlebot visits your pages, which can inform site optimization.
How to check if a link is crawlable?
![]()
Understanding Link Accessibility and Crawlability
To determine if a link is crawlable, it’s important to understand the elements affecting its accessibility. A crawlable link allows search engine bots to follow it, which can help in indexing a website’s pages. Here’s how to ensure a link’s crawlability:
- Ensure the Link is in a Crawlable Format: Verify that the link is a standard HTML link using the `Text` format. Links embedded in scripts (e.g., JavaScript) may not be crawlable.
- Check the Robots.txt File: Make sure that the link’s path is not blocked by your website’s `robots.txt` file. Paths listed under Disallow in this file prevent bots from crawling certain sections.
- Inspect the Meta Tags and HTTP Headers: Ensure that the page containing the link does not have “ tags or HTTP headers set to disallow crawling.
Using Online Tools to Test Link Crawlability
Several online tools can help identify if a link is crawlable by search engines. These tools offer insights into how various elements of your site might impact search engine robots:
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: This tool allows you to crawl your website like a search engine bot, providing detailed information about which links can be crawled and which cannot.
- Google Search Console: Within the URL Inspection tool, inputting a page URL gives insights into its crawlability status and any associated issues.
- Online Robots.txt Testers: These handy tools allow you to input any URL to check against your `robots.txt` rules and see if it is blocked from being crawled.
Analyzing the Website Structure and Linking Practices
Effective website structure and linking practices are crucial for making links crawlable. Consider the following when reviewing your site for optimal crawlability:
- Use a Logical URL Structure: Ensure URLs are clean and reflect the content hierarchy. A structured approach aids bots in navigating through the site.
- Avoid Deep Page Nesting: Links leading to content many clicks from the homepage may be harder for bots to reach. Keep link paths shallow when possible.
- Incorporate Internal Linking: Having a robust internal linking strategy helps bots discover more pages and creates a web of links that promotes crawlability within the site.
How to detect Google crawler?

To effectively detect a Google crawler, it’s essential to identify the characteristics and behavior typical of Google’s search engine bots. Here’s a detailed guide on how to recognize these crawlers.
Understanding User-Agent Strings
To distinguish Google crawlers, analysing the User-Agent string is crucial as it provides identifiable information about the crawler’s identity and purpose.
– Googlebot: This is the most common User-Agent for Google’s web crawler. The typical format is `Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html)`.
– Googlebot-Image: This bot focuses specifically on crawling images for Google Images. Its User-Agent string is `Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Googlebot-Image/1.0; +http://www.google.com/bot.html)`.
– Googlebot-News: Used for crawling articles for Google News. Its User-Agent is `Googlebot-News`.
Verifying IP Addresses
To confirm if a request is indeed from Google, verifying the IP address is an effective measure. Legitimate Google crawlers will originate from Google’s registered IP addresses.
- Check DNS Records: Perform a reverse DNS lookup on the supposed crawler’s IP address. It should resolve to a `googlebot.com` or `google.com` domain.
- Verify Forward DNS: Query the hostname to check if it resolves back to the original IP address. This confirms the authenticity of the hostname.
- Use WHOIS Service: Cross-reference the IP address with a WHOIS service to ensure it belongs within Google’s IP ranges, which are publicly available.
Monitoring Crawling Activity
Monitoring the activities of crawlers on your website provides deeper insights into their behavior, helping you identify Google crawlers more precisely.
- Log Analysis: Regularly analyze server logs to track the frequency and pattern of requests from Googlebots. Identify patterns like a surge in activity when new content is published.
- Google Search Console: Use the Crawl stats feature to get detailed reports on how often your site is crawled by Google, identifying trends and anomalies.
- Access Control: Implement access control rules that log all requests from known IP address ranges, maintaining a record of consistent Googlebot activities.
How to check crawl status?
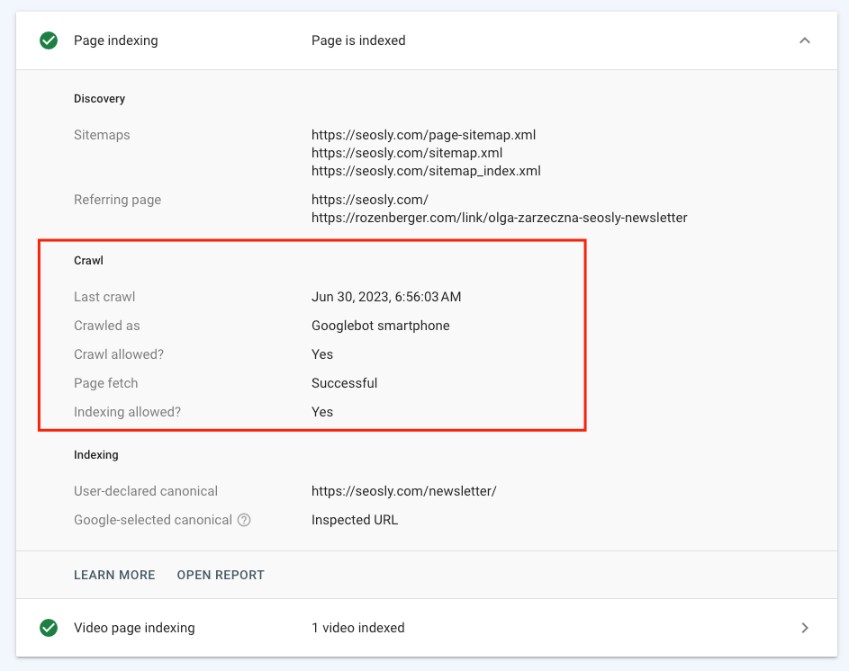
Understanding Crawl Status in Google Search Console
To effectively check your crawl status, using Google Search Console is one of the most common methods. This tool provides insights into how often Google is crawling your site and any potential issues it might encounter.
– Access Google Search Console:
– Navigate to the Google Search Console website and log in.
– Select your website property you wish to check.
– Navigate to Crawl Stats:
– Click on the “Coverage” or “Crawl Stats” under the “Index” section in the left-hand menu.
– This will give you insights into pages crawled per day, kilobytes downloaded per day, and more.
– Review Crawling Details:
– Examine items such as Errors, Valid with warnings, or Excluded to understand crawl status.
– Address any errors that mention server connectivity, URLs marked as noindex, or blocked by robots.txt.
Utilizing Logs to Monitor Crawling Activities
Log files are crucial for understanding how search engines interact with your website. Analyzing these logs can offer a deeper understanding of your site’s crawl status beyond Google Search Console.
– Access Server Logs:
– Obtain access to your website’s server logs through your hosting provider or server admin.
– Ensure you have the necessary permissions to view these logs.
– Identify Bot Activity:
– Look through the logs to identify entries from Googlebot or other search engine bots.
– Pay attention to the frequency and depth of access to various pages on your site.
– Analyze Patterns:
– Use log analysis tools or software to make sense of the data.
– Identify which areas of your site are being crawled most frequently and any potential bottlenecks or issues.
Checking Crawl Status Through Third-Party Tools
In addition to Google Search Console and server logs, third-party tools can provide further insights into your crawl status. These tools offer different perspectives and valuable features for understanding crawl behavior.
– Choose a Reliable Tool:
– Utilize tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider or Ahrefs which provide details on crawl errors, frequency, and data analysis.
– Run a Crawl Analysis:
– Set up your chosen tool to begin crawling your website, ensuring settings reflect those of search engine crawlers.
– These tools often simulate a search engine’s crawl, providing additional insights into how effective and frequent crawling occurs.
– Review and Implement Suggestions:
– Analyze reports generated by these tools to pinpoint crawl issues or optimization opportunities.
– Follow suggestions regarding broken links, missing tags, or duplicate content that can hinder effective crawling.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I check my server logs for Googlebot activity?
To test if Googlebot has crawled your link, one of the first steps is to examine your server logs. Server logs provide a record of all requests made to your website, including those made by Googlebot. Access your server logs, which are typically available through your web hosting provider or web server management software. Once you have access, search for entries with the user-agent string Googlebot. This string indicates that the request originated from Google’s crawler. Additionally, check the IP address to ensure it’s from a Google range, as this confirms the request’s authenticity. Analyzing server logs is a direct and reliable method to verify Googlebot’s interaction with your site.
What tools can assist in confirming a Googlebot visit?
There are several tools available that can help you confirm whether Googlebot has crawled your link. Tools like Google Search Console provide valuable insights regarding how Google interacts with your site. Within Google Search Console, you can utilize the URL Inspection tool to see when Google last crawled specific URLs. Additionally, third-party services like Screaming Frog or SEMrush offer features to monitor and report on crawl activity. These tools can provide details on the frequency and timing of Googlebot visits, helping webmasters understand how their links are being accessed by the crawler.
How can custom Google Analytics reports help determine Googlebot crawling?
Custom Google Analytics reports can be instrumental in determining if Googlebot has crawled your link by tracking traffic patterns and behaviors. While Google Analytics is primarily designed to monitor user activity, you can set up custom filters to differentiate bot traffic. By creating a segment that filters visits from known Googlebot IP ranges or its user-agent, you can generate reports specifying when and how often Googlebot visited your site. However, remember that Google Analytics is designed for tracking user interactions rather than bot activities, so supplementing this method with server log analysis is advisable for more comprehensive insights.
Why is it important to verify Googlebot crawls your link, and what actions should you take?
Verifying that Googlebot crawls your link is crucial because it directly influences your site’s visibility and indexing on Google’s search engine. If Googlebot does not crawl your pages, they might not appear in search results, affecting your site’s organic traffic and SEO performance. To ensure efficient crawling, check your robots.txt file to confirm it’s not inadvertently blocking Googlebot. Also, ensure your sitemap is correctly submitted and updated in Google Search Console. Regularly monitoring your site’s crawl status allows you to address any issues promptly, optimize your site structure, and enhance your overall search visibility.