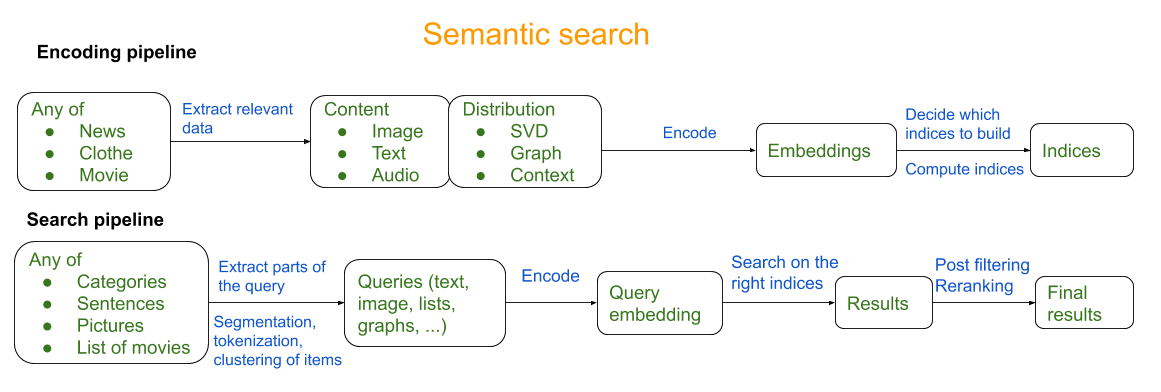
In the rapidly evolving world of digital marketing, staying ahead requires a keen understanding of both technical and creative aspects of SEO. Indexing and Semantic SEO are two critical components that, when intertwined effectively, can significantly enhance a website’s visibility and relevance. Indexing involves the process by which search engines gather and organize information from websites, determining what content appears in search results. Meanwhile, Semantic SEO focuses on the meaning and context behind keywords, aiming to deliver content that matches the intent of search queries. Together, they form a powerful synergy, driving more nuanced and effective search engine optimization strategies.
The Interplay Between Indexing and Semantic SEO
Indexing and Semantic SEO play a crucial role in how websites are understood and ranked by search engines. Successful implementation of Semantic SEO ensures that content is not only visible to search engines but also relevant and comprehensible to users. This relationship between indexing and semantics influences how content is presented and prioritized in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Understanding the Importance of Indexing in SEO
Indexing is the process by which search engines organize and store web pages to later retrieve and present them in response to search queries. Without proper indexing, even the most valuable content may remain invisible to users because it won’t appear in search results. Indexing acts as a foundational element in SEO, determining the visibility and accessibility of a website. Ensuring that your site is correctly indexed involves utilizing tools like Google Search Console to monitor crawling, resolving crawling errors, and submitting sitemaps to assist search engines.
The Role of Semantic SEO in Enhancing Content Relevance
Semantic SEO focuses on improving the searchability of content by aligning it with the intent behind user queries. It goes beyond keyword optimization to provide a deeper understanding of what the content is about, considering the nuances and contexts of language. By implementing Semantic SEO, websites can improve the relevance of their content, making it more visible to search engines that are increasingly leveraging AI to interpret content meaningfully. This involves using structured data, thematic keyword research, and creating context-rich content that resonates with user intent.
How Indexing and Semantic SEO Work Together
While indexing deals with how content is stored and retrieved, Semantic SEO ensures that the content is comprehensible and relevant. Together, they create a symbiotic relationship where well-indexed content benefits from the applied semantic strategies to enhance its search engine visibility. This combination aids search engines in delivering accurate results that satisfy user search intents. Effective cooperation between these two components results in higher search rankings and increased organic traffic.
Challenges in Implementing Indexing and Semantic SEO
One significant challenge in aligning indexing with Semantic SEO is ensuring that dynamic web pages are indexed correctly without losing vital semantic signals. Websites need to handle various obstacles, such as duplicate content, slow page load times, and JavaScript rendering issues, all of which can hinder proper indexing. Additionally, managing semantic markup properly without conflicting with crawlers or existing site architecture is crucial to prevent misinterpretations by search engines. Constant monitoring and quick resolution of these issues are vital for maintaining a healthy SEO strategy.
Best Practices for Combining Indexing and Semantic SEO
To optimize both indexing and Semantic SEO, start with a technical audit to identify any indexing issues. Utilize structured data to enhance semantic understanding and leverage tools like Google Search Console to track the site’s performance. Content should be crafted with a clear understanding of user intent, supported by reliable keyword research. Regularly updating existing content to reflect current trends and ensuring that the site’s back-end technical infrastructure supports both indexing and semantic efforts are also crucial steps. These practices ensure optimal performance of your content in search engine rankings, increasing its accessibility and relevance.
| Aspect | Indexing | Semantic SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Organizes and stores web pages for retrieval. | Improves searchability and relevance based on user intent. |
| Key Focus | Visibility and accessibility in search results. | Relevance and comprehensibility of content. |
| Methods | Crawling, sitemap submission, monitoring via search console. | Structured data, thematic keyword research, context-rich content. |
| Common Challenges | Duplicate content, slow page loading, rendering issues. | Conflicting markup, semantic misinterpretation, staying relevant. |
| Best Practice | Conduct technical audits, resolve crawling issues. | Align content with user intent, update regularly. |
What is the purpose of indexing in semantic search?
The purpose of indexing in semantic search is to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of retrieving meaningful information or documents by understanding the context and intent behind search queries beyond just keyword matching. By organizing and structuring the data, semantic search indexing helps to deliver results that are more relevant by interpreting the user’s needs.
Improving Search Relevance
Indexing improves the relevance of search results by creating an organized repository of information that can be quickly accessed and utilized for matching user queries semantically.
– Contextual Understanding: Semantic indexing enables the search engine to understand the context of words in a document or query, allowing it to provide results that are contextually appropriate.
– Synonym Recognition: By indexing synonyms and related terms, the system can handle queries involving different terminologies more effectively.
– Disambiguation: It helps in distinguishing between different meanings of the same word, resulting in more precise search results.
Enhancing Query Interpretation
Semantic search indexing enhances query interpretation, allowing for more nuanced and meaningful search experiences.
– Conceptual Matching: Rather than matching words, indices allow the engine to match concepts, bridging gaps between vocabulary and user intent.
– Natural Language Processing (NLP): It employs NLP techniques to facilitate understanding of the natural language queries as used regularly by users.
– Intent Recognition: By categorizing information based on potential intents, the indexing process aids in identifying and targeting the user’s actual need behind the search.
Boosting Retrieval Speed and Efficiency
Indexing boosts the speed and efficiency of retrieving documents by organizing and structuring data carefully, which reduces the time taken to access relevant results.
– Quick Access: An indexed database allows for rapid retrieval of data, minimizing the time users spend waiting for search results.
– Reduced Processing Load: Comprehensive indexing diminishes the computational load as less processing is required to match and retrieve suitable results.
– Scalability Improvement: Effective indexing ensures that the search system can scale efficiently, handling large volumes of data without a drop in performance.
What is the difference between SEO and semantic SEO?
Understanding Basic SEO
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is focused on enhancing a website’s visibility and ranking on search engine results pages. Here are some key aspects:
- Keyword Optimization: Traditional SEO heavily relies on identifying and utilizing specific keywords that users are likely to search for, embedding them across content to improve rankings.
- On-Page SEO: This involves optimizing individual web pages such as titles, headings, and meta descriptions to be more search-engine friendly.
- Technical SEO: Ensures that a website meets the technical requirements of modern search engines with the goal of improved organic rankings. This includes elements like site speed, mobile-friendliness, and crawlability.
Diving into Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO takes traditional SEO a step further, by focusing on understanding the intended meaning behind search queries rather than just keywords. Here are its key features:
- Contextual Understanding: Instead of merely targeting exact keywords, semantic SEO considers the context in which keywords are used, making content more relevant to the user’s intention.
- Topic Clusters: It emphasizes creating content organized around central themes or topics, enhancing user comprehension and site structure.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Utilizes NLP to better align content with how users naturally search and how search engines interpret meaningfulness in queries.
Key Differences Between SEO and Semantic SEO
The transition from traditional SEO to semantic SEO marks a shift towards a more holistic approach to content strategy. Key differences include:
- Focus Shift: Traditional SEO focuses on keywords, while semantic SEO prioritizes the complete user intent and richness of content.
- Approach to Content: Traditional SEO might concentrate on a single keyword density, whereas semantic SEO creates a network of related concepts and interconnections.
- Search Engine Evolution: With updates like Google’s Hummingbird, semantic SEO adapts to engines that interpret search queries with a more human-like understanding.
What is the primary goal of latent semantic indexing in SEO?
The primary goal of latent semantic indexing (LSI) in SEO is to improve the relevance and quality of search results by understanding the contextual relationship between words and concepts in content. By utilizing LSI, search engines aim to deliver more accurate and comprehensive results to users beyond simple keyword matching.
The Role of Latent Semantic Indexing in Enhancing Content Relevance
Latent semantic indexing helps search engines determine the context in which words are used, which improves content relevance.
– Contextual Understanding: LSI analyzes the relationship between various terms and concepts within a document, helping search engines understand content beyond isolated keywords.
– Semantic Relationships: By recognizing related terms, LSI enables search engines to match user queries with documents that may not use the exact same keywords but have similar meanings.
– Improved Search Results: This deeper understanding allows search engines to connect users with more relevant content, thereby enhancing the user’s search experience.
How Latent Semantic Indexing Influences Keyword Strategy
The use of latent semantic indexing significantly impacts keyword strategies by encouraging the incorporation of related terms and phrases.
– Expansion of Keywords: LSI prompts content creators to think beyond primary keywords and include semantically related terms to capture a broader scope of user intent.
– Natural Language Usage: With LSI, content should be written in more natural language that aligns with the way users ask questions or seek information.
– Focus on User Intent: Understanding the semantic relationships between terms aids in addressing the actual intent behind user searches, which is crucial for effective SEO strategies.
The Importance of Quality Content in Latent Semantic Indexing
Quality content is central to the effectiveness of latent semantic indexing, as it relies on meaningful and contextually rich content.
– Content Richness: Quality content with diverse vocabulary and in-depth information is more likely to align with LSI principles, aiding search engines in making semantic connections.
– Engagement and Relevance: By focusing on content depth and relevance, sites are more likely to engage users, meeting the goals of LSI to deliver pertinent information.
– Authority and Trustworthiness: Well-structured, authoritative content helps build trust with search engines, increasing the likelihood of better rankings through LSI methodologies.
How has semantic search changed SEO?
Understanding Semantic Search
Semantic search has revolutionized SEO by shifting from purely keyword-based strategies to understanding the meaning and intent behind search queries. This change marks a more sophisticated and intuitive approach to connecting users with the information they seek.
- Context Awareness: Semantic search considers the user’s historical search behavior and preferences to deliver more personalized results.
- Entity Recognition: It identifies and understands entities such as people, places, and objects, providing more relevant results than mere keyword matches.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Utilizes NLP to comprehend the nuances of human language, significantly improving how search engines interpret complex queries.
Impact on Keyword Strategy
The integration of semantic search has caused a transformation in how SEO professionals approach keyword strategy, forcing a shift from isolating individual keywords to prioritizing topics and entity-based optimization.
- Long-Tail Keywords: There’s more emphasis on using long-tail keywords that capture the true intent of the user query rather than focusing on single, broad ones.
- User Intent: SEO now places greater emphasis on understanding and optimizing content based on user search intent, such as informational, navigational, or transactional intent.
- Topic Clusters: A focus on creating content around clusters of topics that address a broad array of relevant queries and concepts, rather than just targeting individual keywords.
Effects on Content Creation
Semantic search has altered how content is crafted, encouraging the development of richer, more engaging, and contextually relevant content to satisfy both search engines and users.
- Content Depth: Creating comprehensive content that covers a range of related topics deeply and thoroughly to satisfy complex search queries and increase authority.
- Structured Data: Implementing structured data markup can help search engines better understand the context of the content, enhancing visibility in search results.
- Engagement Metrics: With semantic search, engagement metrics such as dwell time and bounce rate are considered more heavily, emphasizing the need to retain user interest through engaging content.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Indexing in the Context of SEO?
Indexing in SEO refers to the process by which search engines like Google organize and store web pages they have crawled on their servers. This process is crucial for retrieving and ranking content in response to user queries. When a search engine bot crawls a website, it collects the page’s data, including text, metadata, and structure, to understand its subject matter. This data is then processed, analyzed, and indexed so that the page can be easily retrieved. An indexed page has a higher likelihood of appearing in search engine results when relevant keywords are queried, making indexing a vital component for visibility and traffic acquisition.
How Does Semantic SEO Differ From Traditional SEO?
Semantic SEO is an evolved approach that goes beyond keyword-focused strategies to understand the context and intent behind a user’s search. Unlike traditional SEO, which relies heavily on exact keyword matching, semantic SEO emphasizes the relationships between words and concepts. By optimizing content for semantically related topics and entities, a website can improve its relevance and authority. This approach involves understanding user intent, using rich snippets, structured data, and leveraging LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords. Semantic SEO aims to provide comprehensive, nuanced content that meets user needs more effectively than just targeting specific keywords.
How Are Indexing and Semantic SEO Connected?
Indexing and Semantic SEO are interconnected as both aim to enhance a website’s visibility on search engines, but they do so from different yet complementary angles. By focusing on semantic SEO, content creators provide search engines with a clearer understanding of the page’s context, which improves how the page is indexed. Search engines are designed to offer the most relevant results to users, and a semantically optimized page offers richness and depth that can lead to better indexing. Through the use of structured data and thoughtful content architecture, semantic SEO helps search engines index pages in a way that amplifies their findability and relevancy, aligning them more closely with user intent.
What Strategies Can Enhance Both Indexing and Semantic SEO?
To enhance both indexing and semantic SEO, one should focus on creating comprehensive and user-centric content that addresses the complete array of a topic. Implementing structured data, such as schema markup, can clarify the relationship between entities on a page, aiding search engines in more precisely categorizing and indexing content. Ensuring that the website is technically optimized – including fast load times, mobile responsiveness, and secure HTTPS connections – can facilitate efficient crawling and indexing. Additionally, using internal linking strategically helps distribute link equity across the site, while simultaneously exposing relationships between content that bolster semantic SEO. Finally, regularly updating and auditing content keeps it fresh, relevant, and aligned with current search algorithm expectations.